In today’s digital-first world, OTP authentication plays a vital role in keeping your personal and financial information secure. Whether you’re logging into a bank account, completing a UPI transaction, or verifying your Aadhaar for eKYC, OTPs are everywhere. But what exactly is OTP authentication, and why is it considered one of the safest verification methods?
Let’s break it down.
What Is OTP Authentication?
OTP authentication refers to a security process where a One-Time Password (OTP) is generated and sent to the user to verify identity during login, transactions, or sensitive actions. The OTP is typically valid for a short time and can be delivered via SMS, email, authenticator apps, or hardware tokens. It is commonly used as a form of two-factor authentication (2FA) in banking, digital apps, and enterprise systems.
In essence, it’s a time-sensitive, single-use password that ensures only you can access or approve a digital action.
‘OTP Authentication’ in some of the Indian languages
How You Can Explain ‘OTP Authentication’ to Kids
Think of OTP authentication like a secret code that works only once. Imagine you’re trying to enter a secure building, and someone gives you a new code each time you enter. Even if someone saw your last code, they can't use it again. That’s what OTP does for your online accounts.
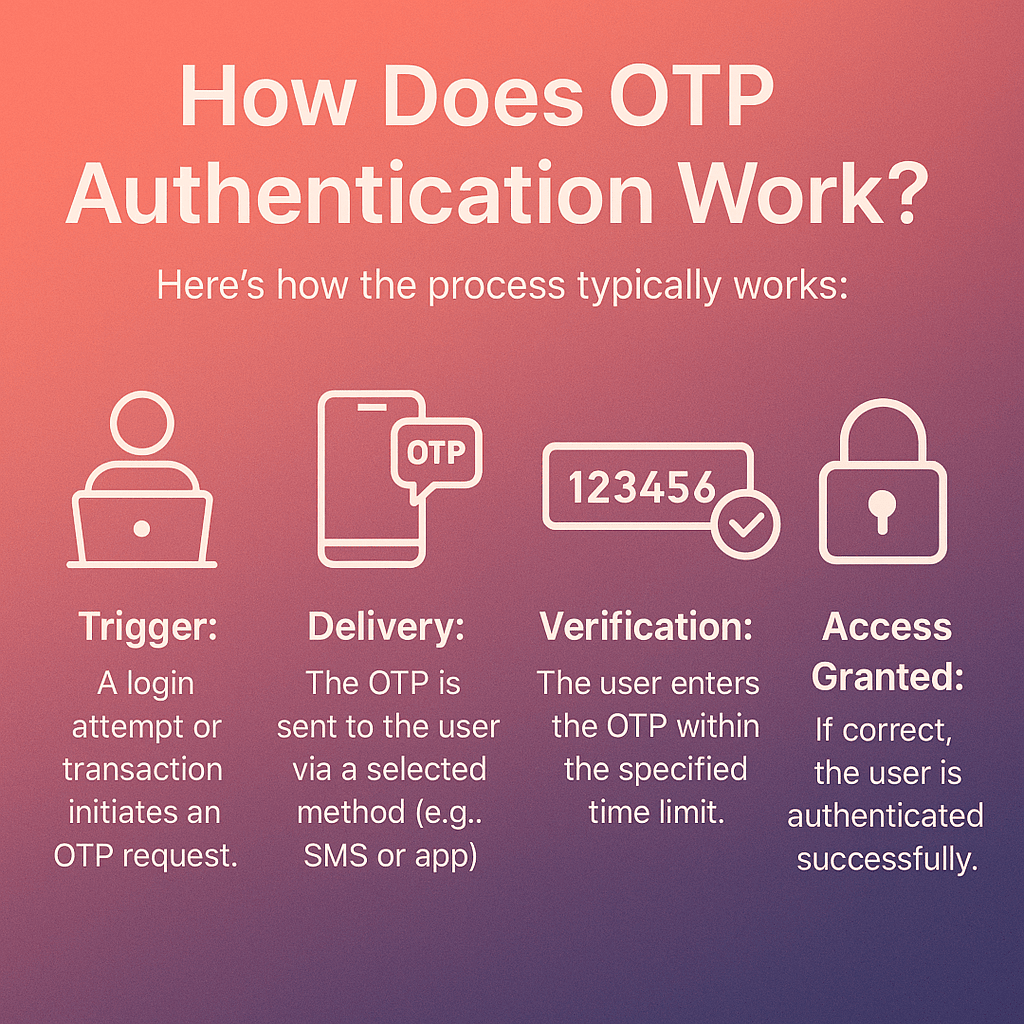
How Does OTP Authentication Work?
Here’s how the process typically works:
- Trigger: A login attempt or transaction initiates an OTP request.
- Delivery: The OTP is sent to the user via a selected method (e.g., SMS or app).
- Verification: The user enters the OTP within the specified time limit.
- Access Granted: If correct, the user is authenticated successfully.
This method is widely used in India for:
- Net banking and mobile banking
- UPI apps like Jupiter, PhonePe, Paytm, Google Pay
- Aadhaar eKYC verifications
- Online shopping and bill payments
Types of OTPs: SMS, Email, App, Hardware Token
OTP vs Password vs Biometric Authentication
- Passwords are static and reused, making them easier to compromise.
- OTP authentication adds dynamic, single-use passwords that change every session.
- Biometric authentication (like fingerprint or face ID) is based on physical identity.
Many systems use OTP as part of Two-Factor Authentication (2FA), combining something you know (password) and something you have (OTP) for higher security.
Time-Based vs Counter-Based OTPs
There are two main types of OTP algorithms:
- TOTP (Time-Based One-Time Password): Changes every 30 seconds. Used by apps like Google Authenticator.
- HOTP (HMAC-Based One-Time Password): Generates OTP based on a counter that increments with every login attempt.
TOTPs are more common in consumer apps, while HOTPs are often used in enterprise systems like LDAP or VPN logins.
Note:
HMAC full form is Hash-based Message Authentication Code
LDAP full form is Lightweight Directory Access Protocol
OTP Authentication in India: Real-World Use Cases
In India, OTPs are a default security mechanism across:
- Banking: For fund transfers, cardless withdrawals
- UPI: To authorize payments and register new devices
- Aadhaar: eKYC for telecom, banking, and income tax e-filing
- E-commerce: To approve payments and logins
- Corporate Systems: LDAP authentication, VPN access, employee logins
OTP Authentication vs Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
OTP can be:
- A single-factor authentication (like OTP login without password)
- A second factor in a 2FA system, enhancing security when used with passwords or biometrics
Some of the Best OTP Authenticator Apps & OTP Managers
Here are some of the top tools for managing OTPs securely:
- Google Authenticator
- Microsoft Authenticator
- Authy (Twilio)
- DUO Mobile
- FreeOTP
- YubiKey (hardware-based)
These apps work offline and provide time-based OTPs, making them more secure than SMS-based OTPs which are vulnerable to SIM swap attacks.
FAQs on OTP Authentication
Q1. What is OTP authentication?
OTP authentication is a security process that uses a one-time password to verify a user’s identity for login or transactions.
Q2. How does SMS OTP verification work?
An OTP is sent to your mobile number. You enter it within a time window to verify your action or identity.
Q3. What is the difference between TOTP and HOTP?
TOTP is time-based (changes every 30 seconds). HOTP is counter-based (increases with each login attempt).
Q4. Are OTP authenticator apps better than SMS OTP?
Yes. They are more secure, work offline, and avoid risks like SMS interception or SIM swap fraud.
In this article
 Back to all resources
Back to all resources





